What is Compound Interest?

Imagine a financial force so potent that even a modest investment can snowball into a substantial nest egg over time. That’s the magic of compound interest—a silent engine powering the growth of your savings and investments. In today’s financial landscape, understanding how your money can earn interest on interest is not just a neat trick; it’s a game changer for long-term financial success. This blog will demystify the concept of compound interest, explain how it works, and reveal why it matters for anyone looking to build lasting wealth.
Try Traconomic’s Free online Compound Interest calculator!
1. Defining Compound Interest
At its core, compound interest is a dynamic process where your money earns interest on both the original principal and on the interest that has already been accumulated over time. Instead of simply earning a fixed percentage on your initial deposit, each interest calculation builds upon the previous one, setting the stage for a self-reinforcing cycle of growth. This phenomenon isn’t linear—it’s exponential. As the earned interest gets reinvested, it creates a snowball effect that accelerates the growth of your investment, transforming modest beginnings into significant sums over the long run

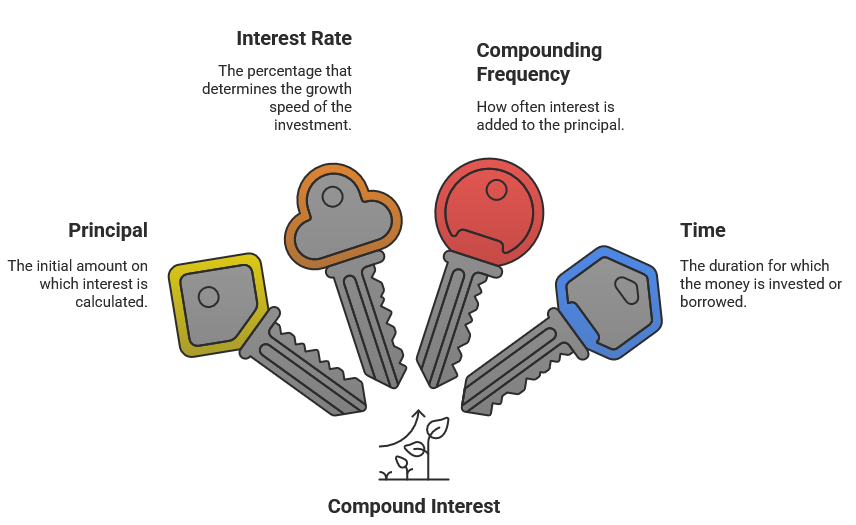
2. Key Components of Compound Interest
Understanding compound interest requires breaking it down into its fundamental building blocks. You are going to learn about the:
- Interest Rate (r):
The percentage that determines how quickly your money grows. It’s expressed as a percentage per period (usually annually), and even small differences in the rate can have a dramatic impact over time. - Compounding Frequency (n):
The number of times interest is added to the principal within a year. Whether it’s compounded annually, semi-annually, quarterly, or monthly, the frequency can significantly influence the growth of your investment. - Time (t):
The duration for which the money is invested or borrowed, typically measured in years. The longer the time period, the more opportunities there are for the compounding effect to work its magic.
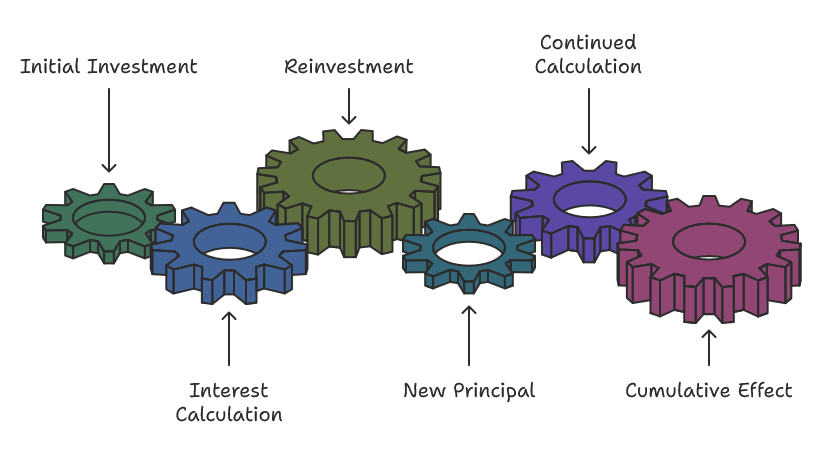
3. How Compound Interest Works
Step 1: Initial Investment
Your journey with compound interest begins with the initial deposit, known as the principal. This is the foundational sum of money that sets the stage for all subsequent growth. Whether you’re investing in a savings account or starting a portfolio, this starting amount is critical as it forms the basis for every future calculation.

Step 2: Interest Calculation

At the end of each compounding period, interest is computed based on the current principal. Unlike simple interest, where calculations are made solely on the initial deposit, compound interest includes all accumulated interest in its calculation. This means that for each period, the interest earned is proportional to the entire amount available at the beginning of that period.
Step 3: Reinvestment
Once the interest is calculated, it isn’t simply paid out or set aside; it’s added directly to the principal. This reinvestment step is crucial because it creates a new, larger principal amount. By merging the earned interest with the original deposit, you enable the next round of interest calculations to be based on a higher sum, paving the way for accelerated growth.

Step 4: Repetition and Exponential Growth
The cycle repeats with each compounding period:
- New Principal: The updated principal, now larger due to the reinvested interest, is used for the next calculation.
- Continued Calculation: Interest is computed on this increased sum.
- Cumulative Effect: Over time, this continuous reinvestment leads to exponential growth. Each cycle builds upon the previous one, so the rate of increase accelerates as the principal grows.
This repetitive process is what makes compound interest such a powerful financial tool. It can transform a modest investment into a substantial sum over time, underscoring its significant impact on long-term savings and investment strategies.
4. The Compound Interest Formula
Ever wonder how a modest investment can transform into a financial powerhouse over time? Welcome to the magic of compound interest! Here’s the formula that makes it all happen:
\[ A = P \left( 1 + \frac{r}{n} \right)^{nt} \]
Where:
A: This is your grand finale—the total amount after your investment has run its course. It’s your initial cash plus all the interest that’s been piled on.
P: Your starting point, or principal—the initial sum you kick off your financial journey with.
r: The annual interest rate, but don’t forget to convert it into a decimal. So, a 5% rate becomes 0.05
n: How often your interest gets to work its magic in a (usually) year. Whether it’s annually, quarterly, or monthly, the more often it compounds, the bigger the boost.
t: The time your money gets to grow, measured in (also usually) years. Patience is key here—the longer you wait, the more dramatic the effect.
Now, how do we pinpoint just the extra cash earned?
Simply subtract your original principal from the total amount:
Compound Interest = A – P
This easy and simple calculation reveals the secret power: reinvesting your earned interest turns your money into a self-growing machine, with every cycle boosting your financial firepower. It’s the kind of exponential growth that can turn even a small investment into a success story.
5. Examples and Applications
Compound interest isn’t just a dry financial concept—it’s a dynamic force that shapes our everyday financial lives. Here’s how it plays out in different scenarios:
Savings Accounts
Banks use compound interest as a magic multiplier for your deposits. Each time interest is added to your balance, it joins the principal for the next calculation. This means your savings grow faster over time, even if you’re starting with a modest sum. It’s like having your money work overtime, quietly building a financial cushion with each passing year.
Investments
When it comes to investing, compound interest is the secret ingredient that can turn small, regular contributions into substantial wealth. By reinvesting dividends and interest, your earnings aren’t just added on—they themselves begin to earn more. Whether you’re putting money into mutual funds, retirement accounts, or other investment vehicles, this snowball effect can lead to impressive, exponential growth over the long run.
Loans
On the flip side, compound interest can also work against you in the realm of debt. With loans, if you don’t keep up with the interest payments, the accumulated interest is added to the principal. This means you could end up paying interest on a larger amount than you initially borrowed. It’s a stark reminder of why understanding the terms of your loan is critical—especially the compounding frequency—to avoid the trap of escalating debt. We have not covered the topic yet,but you might want to read more about this on investopedia.

6. Visual / Scenario Example
Consider this scenario: You start with an initial deposit of $1,000 in a savings account offering a 5% annual interest rate, compounded annually. Here’s how it unfolds:
Year 1:
\[ A = 1000 \times \left(1 + \frac{0.05}{1}\right)^{1 \times 1} = 1000 \times 1.05 = 1050 \]
Your balance grows to $1,050.
Year 2:
\[ A = 1050 \times 1.05 \approx 1102.50 \]
After the second year, you’re looking at roughly $1,102.50.
In this way, each year your balance isn’t just increasing by a fixed amount—it’s growing on itself, leading to a powerful, exponential effect. This scenario perfectly illustrates how compound interest transforms a small, initial deposit into a significantly larger sum over time. If you would like to implement it yourself in an excel spreadsheet, here is a great tutorial to follow.
By understanding and leveraging the power of compound interest, you could make smarter decisions in saving, investing, and even managing debt, turning everyday financial choices into opportunities for long-term growth.
7. Conclusion
Compound interest is more than just a financial formula—it’s a dynamic engine of exponential growth. In essence, it takes your initial investment and, by adding interest on top of interest over repeated cycles, transforms it into a significantly larger sum over time. The formula is the roadmap to understanding this phenomenon. It lays out a clear path: start with your principal, let the interest work its magic through regular compounding, and watch as your money builds upon itself.
This powerful concept holds immense implications. On the bright side, compound interest is the secret weapon for growing wealth, whether in savings accounts, retirement funds, or investment portfolios. Conversely, it serves as a cautionary tale when it comes to managing debt—without careful control, compounding interest can escalate what you owe in a surprisingly short time.
Now, it’s time to take action. Dive deeper into the concept, experiment with different scenarios, and see firsthand how small, disciplined financial choices can lead to substantial gains. Whether you’re planning for the future or managing current obligations, harnessing the power of compound interest can be a game changer for your financial strategy.

Related Posts
© Copyright 2025 - All Rights Reserved